FAQs
This page lists out some of the common errors that you might encounter and how they might look like on our systems.
Plotting Large Scaling Results Manually
The following instructions show how to plot large scaling results manually from a collection of .csv files.
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install jureap
jureap manual --input <input-dir> --output <output-dir> [--skip-weak-scaling] [--legend-position x,y ]
The <input-dir> directory contains all the csv files that you want to generate plots for.
The <output-dir> directory will contain the generated plots. basename.
The –skip-weak-scaling flag is optional and should be used if you want to skip plotting weak scaling error bars.
The –legend-position option is optional and should be used if you want to specify the position of the legend in the plot to prevent it from overlapping with your figures. The x and y values can be numeric values between 0 and 1.
Each
.csvfile should be accompanied by a.workloadfile with the sameThe workload file should contain the workload factor. for the
.csvfile. For example, data/strong.tiny.csv should have a corresponding data/strong.tiny.workload file which should contain a single number which is the workload factor.
Partially Failed CI Pipeline
If only a part of the CI pipeline fails, it might be beneficial to avoid rerunning the entire pipeline. However, the current exacb infrastructure for plotting does not support rerunning only the failed jobs. Despite this limitation, you can still rerun only the failed jobs. We are actively working on adding a plotting feature that will support displaying results from multiple runs.
Empty CI Pipeline
If one has commented out all the CI/CD components in the .gitlab-ci.yml
file, then the CI pipeline will be empty and cause an error on the Gitlab CI.
This can be worked around by always having a dummy job in the pipeline like
shown below
dummy_job:
tags: ["docker"]
script:
- echo "Hello, World!"
This will ensure that the pipeline is never empty and will always run.
Partition Split on JUBE
Sometimes you would like to run a benchmark run on two different partitions
like dc-gpu and dc-gpu-large on JURECA. This can be achieved
by writing code like shown below in your JUBE file
- name: queue
tag: jureca
mode: python
_: '"dc-gpu" if int("${nodes}") < 32 else "dc-gpu-large"'
- name: queue
tag: juwels_booster
mode: python
_: '"largebooster" if int("${nodes}") >= 384 else "booster"'
In such cases, make sure that you remove the old code that you have written to set the queues which might look like shown below
- name: queue
tag: dc-gpu
mode: python
_: "dc-gpu"
Increase CI Timeout
Sometimes, your CI job can fail because your CI job is waiting for the the SLURM scheduler to allocate resources for your job, and that process can take much longer than the default timeout of 1 hour. To fix this, you can increase the timeout of your CI job by going to Settings -> CI/CD -> General pipelines -> Timeout and then changing the value to a higher value. We recommend 7d which is 7 days.
Switch to v3 Branch
If you have followed the original instructions of the tutorial, you are most
likely using the main branch which can be checked by looking at value
after the @ symbol when including the component as shown below
and also here
include:
- component: gitlab.jsc.fz-juelich.de/exacb/catalog/jureap/jube@v3
and in order to switch to the v3 branch, you will need to change the value
main to v3 like shown below
include:
- component: gitlab.jsc.fz-juelich.de/exacb/catalog/jureap/jube@v3
You can see this being used in the comprehensive example.
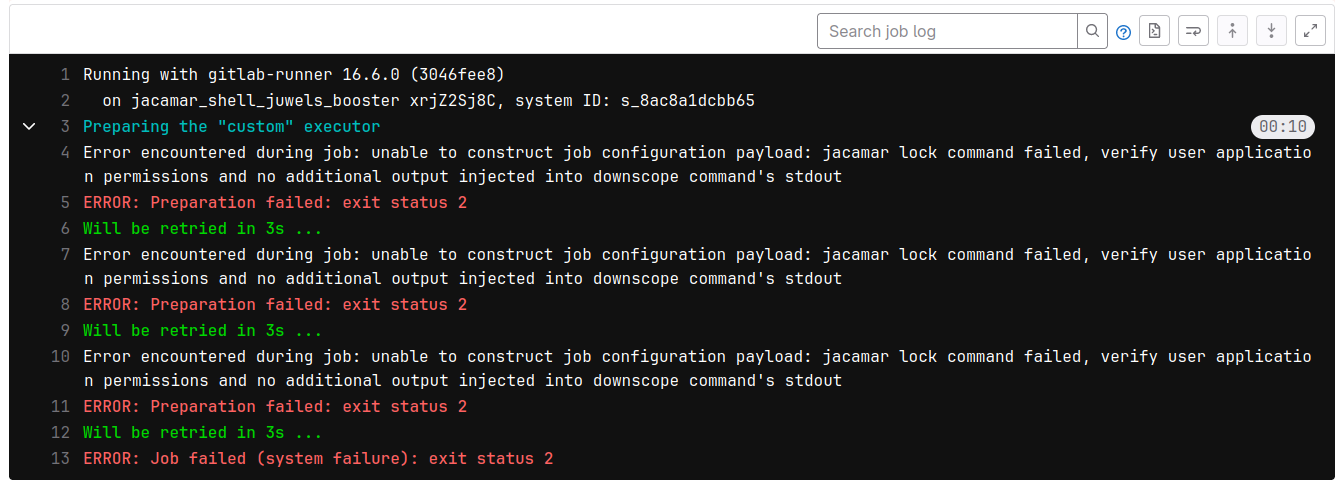
Incorrect SLURM Project
If you try to submit a CI/CD job with a project that you do not have permissions to, then
your CI/CD runner will not be able to create the temporary directories needed to run the job
and you will get a permissions error which will look like the following. To fix
this error, you will need to update the project field in your
.gitlab-ci.yml file to a project that you have write access to.
Disabling Specific CI/CD Jobs
One may want to disable specific CI/CD jobs for a specific commit without
wanting to comment out or delete the code for the job in the
.gitlab-ci.yml file. This can be achieved by using the
rule functionality in Gitlab
CI/CD.
As an example, to unconditionally disable a job, you can use the following rule:
job_name:
script:
- echo "Hello, World!"
rules:
- when: never
and then to unconditionally enable the job again, you can change the value
never to always like follows:
job_name:
script:
- echo "Hello, World!"
rules:
- when: always
You can see this being used in the quickstart example.
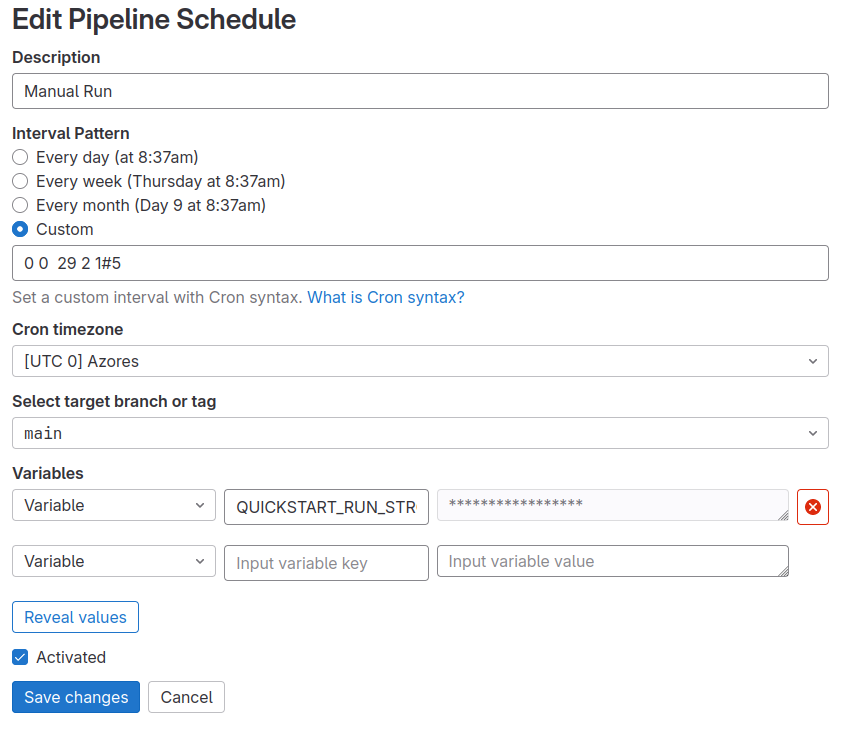
Manually Scheduling Jobs
One might like to schedule some jobs to only run manually. While we are not
currently aware of a native way to do this in Gitlab CI/CD, you can achieve
an approximation of the required task by creating a pipeline that only runs on
29th of February. this can be done by going to Build -> Pipeline
Schedules and then configuring the pipeline like shown below. The pipeline can
then be triggered manually whenever needed. You can see this being used in
here.